Dsm V Definition of Intellectual Disability
The American Psychiatric Association issued the updated manual which mental health care practitioners researchers and insurers rely on. Intellectual disability 1 involves problems with general mental abilities that affect functioning in two areas.

Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria For Developmental Coordination Disorder 6 Download Table
DSM-5 Intellectual Disability Is not defined by psychometric test score alone In other words Intellectual Disability is not defined solely by low full-scale IQ score on IQ test ie IQ 70 In practice many clinicians do not assess adaptive functioning or discount it if the full-scale IQ score was 70-75 or higher 26.

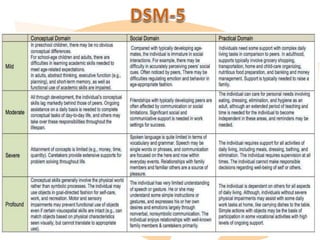
. Chapter 7 DSM-5 and Civil Competencies. A summary of the diagnostic criteria in DSM-5 are as follows. P33 individuals with intellectual disability are characterized by the presence in significant deficits in both intellectual functioning and adaptive behaviour.
This should be measured with an individualized standardized culturally appropriate. Deficits in intellectual functioning. Intellectual disability intellectual developmental disorder formerly mental retardation is characterized by deficits in general mental abilities such as reasoning problem solving planning abstract thinking judgment academic learning and learning from experience.
Under the Americans with Disabilities Act ADA a disability includes a mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities of such individual 42 US. Adaptive functioning activities of daily life such as communication and independent living. Associated with a known medical or genetic condition or environmental factor Coding note.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-Fifth Edition DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for intellectual disability ID include a change to the definition of adaptive impairment. The EEOC recognizes the American Psychiatric Associations Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM as relevant for identifying these disorders. Use additional code to identify the associated medical or genetic condition Associated with another neurodevelopmental mental or behavioral disorder.
In DSM-5 American Psychiatric Association 2013. Chapter 6 DSM-5 and Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity and Diminished Mens Rea Defenses. Chapter 9 DSM-5 and Disability Evaluations.
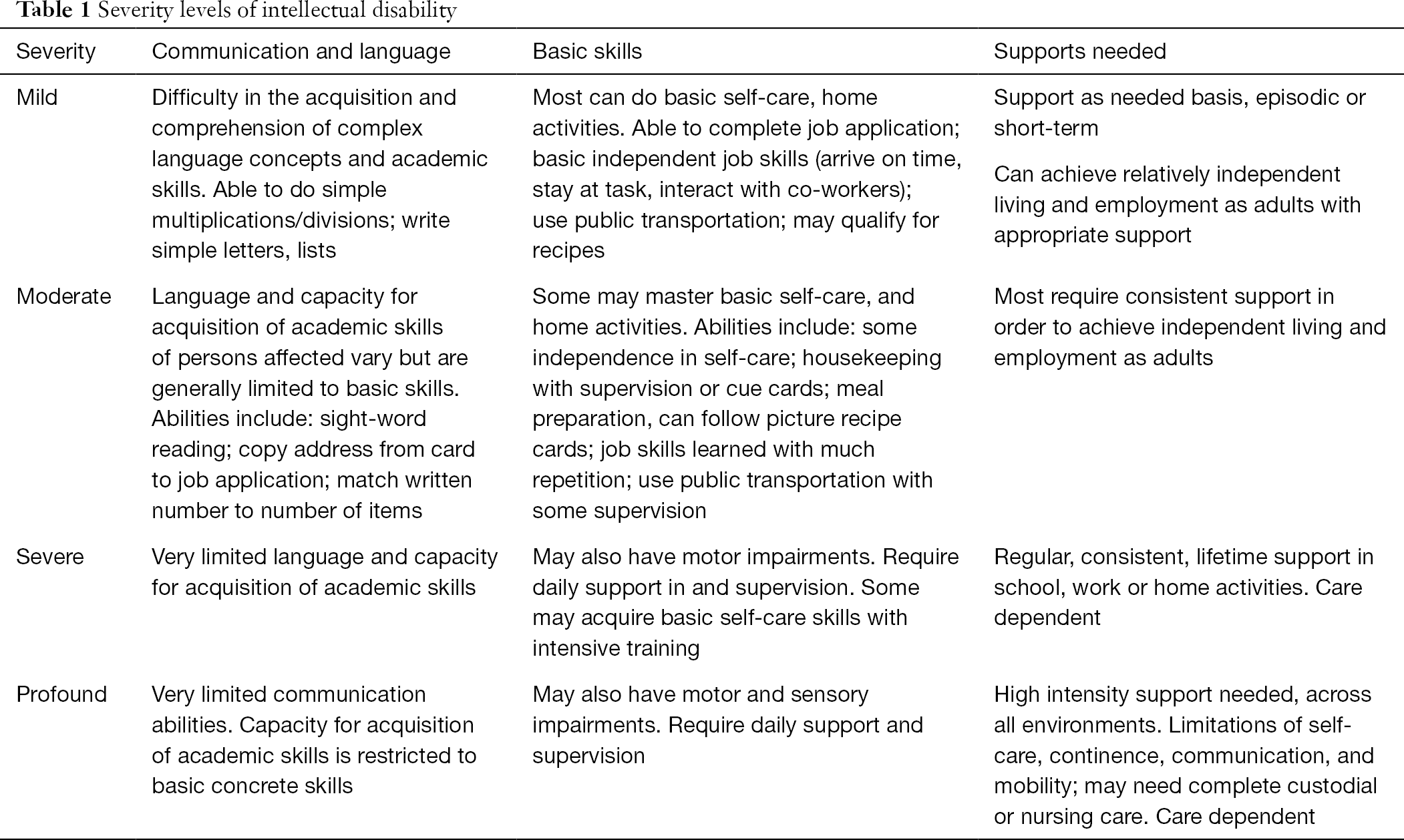
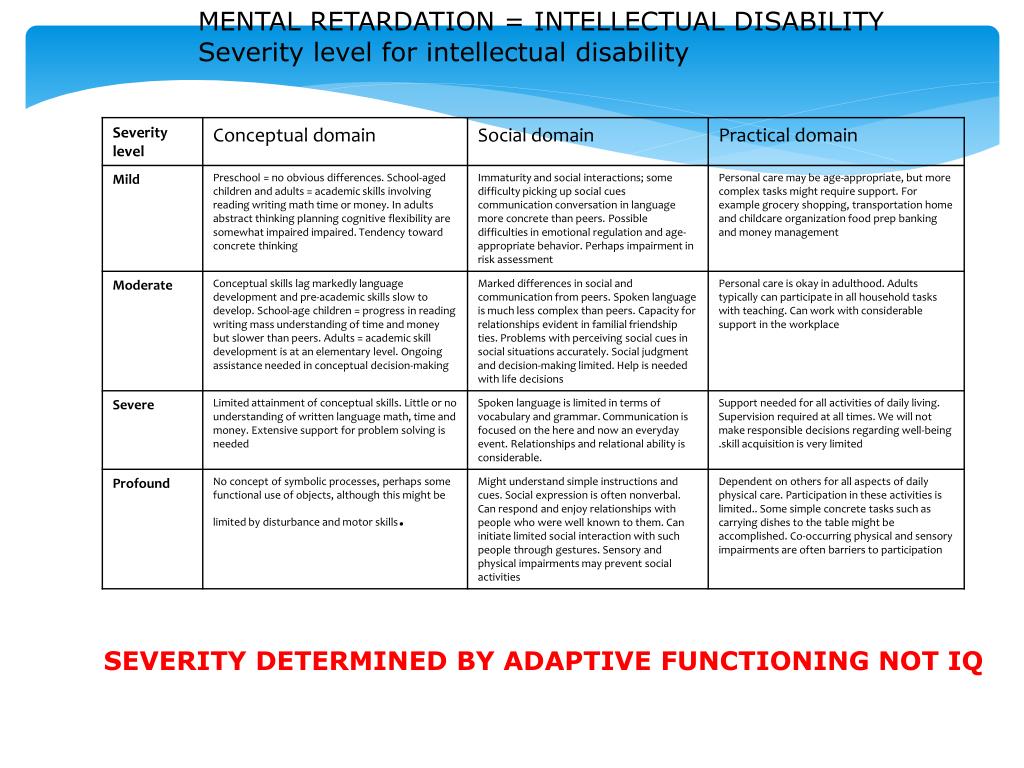
Mild intellectual disability moderate intellectual disability severe intellectual disability and profound intellectual disability. Mild Moderate Severe Profound Based on IQ level DSM 5 Deficits in general mental abilities Impairment in adaptive functioning for the individuals. Current intellectual deficits of two or more standard deviations below the population mean which generally translates into performance in the lowest 3 of a persons age and cultural group or an IQ of 70 or below.
The American Psychiatric Associations APA diagnostic criteria for intellectual disability ID formerly mental retardation are found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-5 APA 2013. In DSM-5 intellectual disability is considered to be approximately two standard devia- tions or more below the population which equals an IQ score of about 70 or below. To meet diagnostic criteria for intellectual disability the deficits in adaptive functioning must.
With or without accompanying intellectual impairmentWith or without accompanying language impairment. Intellectual Disability DSM IV TR IQ 70 or below Concurrent deficits or impairments in present adaptive functioning The onset is before age 18 years Severity. The DSM-5 diagnosis of ID requires the satisfaction of three criteria.
DSM-5 defines intellectual disabilities as neurodevelopmental disorders that begin in childhood and are characterized by intellectual difficulties as well as difficulties in conceptual social and practical areas of living. Intellectual functioning such as learning problem solving judgement. Chapter 8 DSM-5 and Personal Injury Litigation.
New criteria require impairment in one adaptive domain rather than two or more skill areas. Deficits in intellectual functioning. Chapter 10 DSM-5 and Education Evaluations in School-Aged Children.
Definition and DSM 5. This includes various mental abilities. DSM-V places less emphasis on the degree of impairment ie.
The term intellectual disability is the equivalent of intellectual development disorders which was adopted in the draft ICD-11. DSM 5 Intellectual Disability A. T he deficits result in impairments of adaptive.
A new version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders released this month includes changes to the definitions of both autism and intellectual disability that experts say will further clarify the diagnoses. Disorders 5th edition DSM-V Intellectual disability intellectual developmental disorder is a disorder with onset during the developmental period that includes both intellectual and adaptive functioning deficits in conceptual social and practical. To emphasize an increasing convergence between the two classificatory systems this second term has been reported in brackets in the title of the chapter of the DSM.
These children may take longer to walk talk and take care of themselves than the typical. The American Psychiatric Associations APA diagnostic criteria for intellectual disability ID formerly mental retardation are found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-5 APA 2013. Intellectual disability refers to limitations in intellectually functioning and adaptive behavior that have an onset in childhood before age 18.
A summary of the diagnostic criteria in DSM-5 are as follows. Experts divide the types of cognitive impairment into four categories. The authors examined the diagnostic implications of using a popular adaptive skill inventory the.
The assessment of intelligence across three domains conceptual social and practical will ensure that. The term intellectual disability refers to a condition in which a person has certain limitations in intellectual functions like communicating taking care of him- or herself and has impaired social skills. The degree of impairment from an intellectual disability varies widely.
These limitations cause a child to intellectually develop more slowly than other children. IQ scores and more on the. The distinction between learning disabilities and an intellectual impairment has been considered a key issue as it can provide insights about potential for learning and types of interventions appropriate for each group.
Competencies and the Criminal Justice System.

Intellectual Disability And Developmental Disability Understanding And Supporting Learners With Disabilities

Intellectual Disability Signs And Symptoms Mental Retardation Child Development Theories Developmental Disabilities

Intellectual Disability Dsm5 Pdf Free Download
Functional Language Goals For Intellectual Disabilities

Intellectual Disability Intellectual Developmental Disorder Ppt Download

Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria For Developmental Coordination Disorder 6 Download Table

Apa Dsm 5 Intellectual Disability Pdf Intellectual Disability Dsm 5

Intellectual Disability Part I

Children Young People With Intellectual Disability Mental Health Challenges Recent Developments Jeremy Turk Institute Of Psychiatry King S College Ppt Video Online Download
Pdf Intellectual Disability In International Classification Of Diseases 11 A Developmental Perspective

Facing Autism In New Brunswick Autistic Disorder S Twin Intellectual Disability In The Dsm5
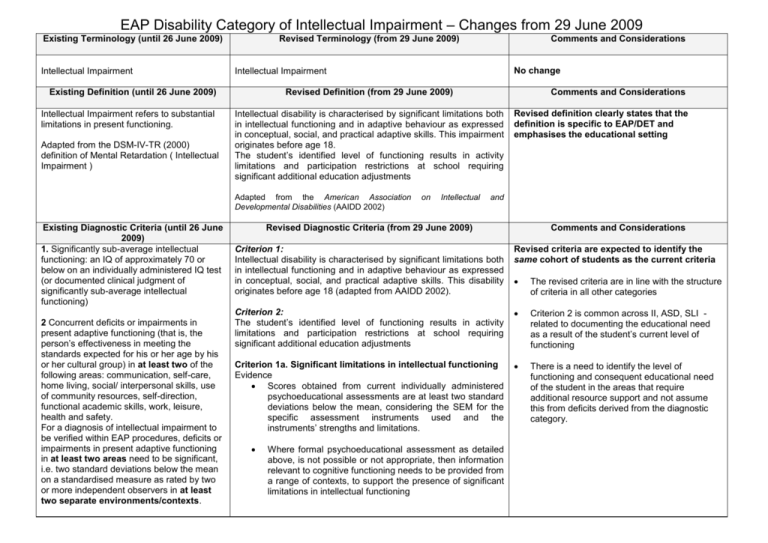
Comparison Of Current Diagnostic Criteria With Proposed Criteria

Highlights Of Changes Dsm Iv Tr To Dsm 5 Ppt Video Online Download
Ppt Diagnostic Groupings In The Dsm 5 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5177310

Pdf Changes In Intellectual Disability In Dsm 5

Dsm 5 Asd Diagnostic Criteria And Specifiers Download Scientific Diagram

Comments
Post a Comment